Best US Hotels for Corporate Retreats in 2026: Strategic Venues for the Future of Work
Corporate retreats in the United States have entered a new phase in 2026, evolving from occasional off-site gatherings into carefully curated strategic interventions that shape culture, sharpen competitive advantage, and sustain high-performing teams over the long term. For the business readership of usa-update.com, which closely follows developments in the economy, employment, technology, regulation, and lifestyle, the question of where to hold a corporate retreat is now inseparable from broader questions of organizational strategy, talent retention, innovation, and brand positioning. The choice of hotel or resort is no longer a purely logistical or hospitality decision; it is a decision about the environment in which leadership alignment, cross-functional collaboration, and creative problem-solving are most likely to thrive.
In the post-pandemic, hybrid-work era, executives across the United States, Canada, Europe, and Asia have recognized that physical proximity still matters when it comes to building trust, resolving complex issues, and setting long-term direction. While videoconferencing tools and digital collaboration platforms have revolutionized day-to-day operations, they have not replaced the need for periodic in-person immersion. As a result, corporate retreats have moved to the center of workforce strategy, particularly for companies operating in highly competitive sectors such as technology, finance, healthcare, energy, and advanced manufacturing. Readers who follow broader business and strategy trends can explore how these shifts intersect with corporate performance on usa-update.com/business, where retreat planning increasingly appears alongside discussions of mergers, innovation pipelines, and leadership transitions.
Corporate Retreats as Strategic Assets in 2026
By 2026, corporate retreats are widely seen as strategic assets rather than discretionary perks. Human resources leaders, chief people officers, and CEOs are using retreats to address several converging business realities: the need to integrate geographically dispersed teams, the pressure to accelerate digital transformation, and the imperative to support employee well-being in an era of constant change. In North America and across global hubs in Europe and Asia, organizations now treat retreats as structured programs with measurable outcomes rather than loosely planned getaways.
The most effective retreats are designed around clear business objectives-such as aligning on a five-year growth strategy, integrating an acquired company, accelerating innovation in a new product line, or re-anchoring culture after rapid headcount expansion. Hotels that cater to this demand have invested heavily in flexible meeting environments, hybrid collaboration technologies, and on-site facilitation support, ensuring that leadership teams can move seamlessly from plenary strategy sessions to smaller breakouts and one-to-one coaching conversations. Many of these properties now employ or partner with professional facilitators, executive coaches, and wellness experts, creating a holistic ecosystem that supports cognitive performance and emotional resilience.
This evolution reflects a broader recognition that corporate performance is tightly linked to the quality of human interaction. Leaders who regularly monitor macroeconomic developments on usa-update.com/economy will recognize the connection between retreat investment and long-term competitiveness: organizations that invest in alignment, culture, and talent development are better positioned to navigate volatility, regulatory shifts, and global competition from Europe, China, and emerging markets.
What Defines a World-Class Corporate Retreat Hotel Today
The best US hotels for corporate retreats in 2026 share several defining characteristics that go far beyond traditional luxury. They are built around four core pillars: strategic functionality, technological sophistication, sustainability, and human-centric wellness. Each pillar directly supports the Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness that business leaders demand from their partners.
World-class properties now offer meeting environments that can be rapidly reconfigured to support design sprints, confidential board discussions, cross-border project reviews, and innovation hackathons. These spaces are equipped with advanced audiovisual systems, secure networking infrastructure, and collaboration tools that support hybrid participation, allowing executives to join critical sessions in real time. Leading hospitality groups have integrated these capabilities into their core offerings, recognizing that corporate clients will not tolerate connectivity gaps or technology failures during high-stakes retreats. For a deeper perspective on how technology infrastructure is reshaping business operations, readers can visit usa-update.com/technology.
Sustainability has also become a non-negotiable criterion. Companies that report under increasingly stringent ESG frameworks in the United States, the European Union, and other jurisdictions are choosing hotels that can demonstrate credible environmental performance, from energy-efficient building systems and renewable energy sourcing to water conservation and waste reduction. Many top-tier properties now align with global initiatives such as the U.S. Green Building Council's LEED certification program or the Global Sustainable Tourism Council's sustainability standards, giving corporate clients confidence that their retreat spending is consistent with stated climate and sustainability commitments. Executives who follow developments in sustainable energy and infrastructure can contextualize these choices alongside broader sector trends on usa-update.com/energy.
Equally important is the integration of wellness into the retreat design. In 2026, high-performing organizations understand that cognitive performance, creativity, and resilience are closely linked to physical and mental well-being. Hotels that specialize in corporate retreats have therefore expanded their wellness offerings beyond spas and fitness centers to include guided mindfulness sessions, structured movement breaks between meetings, nutrition-focused menus, and outdoor experiences designed to reduce stress and strengthen interpersonal bonds. This aligns with research shared by organizations such as the American Psychological Association, which highlights the impact of stress management and workplace support on employee performance and retention; those interested can review current workplace well-being insights through the association's work and well-being resources.
Regional Strengths: Matching Location to Corporate Objectives
Because the United States offers an unparalleled diversity of landscapes, cultures, and business ecosystems, the choice of region has become a strategic decision in itself. Companies are no longer simply asking which hotel is most convenient; they are asking which regional context best supports the message they want to send and the experience they want to create.
On the East Coast, properties in New York, Boston, Washington D.C., and Palm Beach continue to attract organizations that seek a blend of financial gravitas, cultural sophistication, and access to policymaking. Hotels such as The St. Regis New York, The Pierre, A Taj Hotel, The Hay-Adams, and The Breakers Palm Beach provide environments where executives can move from high-level board discussions to meetings with investors, regulators, or policy experts. Their proximity to major financial markets, universities, and government institutions makes them particularly suitable for retreats that involve capital markets strategy, regulatory risk assessment, or public affairs planning. Readers who monitor regulatory developments and policy shifts can connect these location choices with ongoing changes in the US regulatory environment on usa-update.com/regulation.
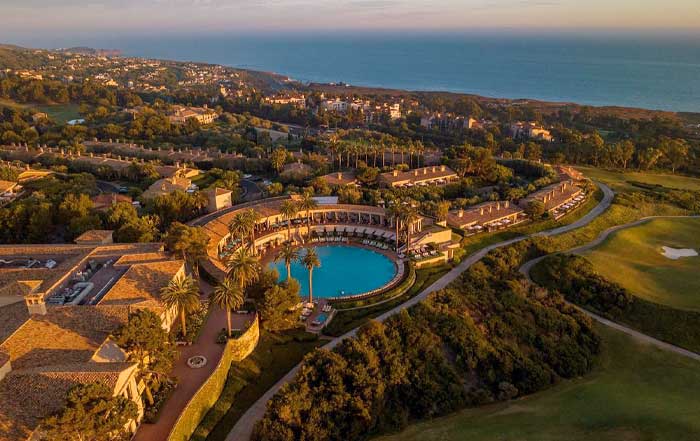
The West Coast, by contrast, is often selected for retreats that emphasize innovation, creativity, and technology-led transformation. Properties such as The Ritz-Carlton, Laguna Niguel, Terranea Resort, Cavallo Point Lodge, The Fairmont Olympic Hotel, and The Resort at Pelican Hill draw companies from the technology, media, and entertainment sectors, as well as global firms that want to immerse their teams in the culture of experimentation associated with California and the Pacific Northwest. The combination of ocean views, outdoor activities, and proximity to innovation hubs in Silicon Valley, Seattle, and Los Angeles helps reinforce strategic themes such as digital reinvention, product innovation, and customer-centric design. For executives following developments in US and global technology ecosystems, usa-update.com/technology offers additional context on why West Coast retreats remain particularly attractive to high-growth firms.
In the Southern United States, retreats often emphasize hospitality, relationship-building, and cultural richness. Venues such as The Cloister at Sea Island, The Houstonian Hotel, Club & Spa, JW Marriott Austin, Four Seasons Resort Orlando at Walt Disney World Resort, and The Peabody Memphis provide a mix of warm climate, regional cuisine, and approachable luxury that supports both serious strategic work and informal networking. These properties are especially attractive to companies with large operational footprints in Texas, Florida, and the broader Sun Belt, where economic and population growth have accelerated in recent years. Business readers who track regional economic shifts and demographic trends across the South will find complementary analysis on usa-update.com/economy and usa-update.com/news.
The Midwest offers a different value proposition: connectivity, affordability, and cultural depth without the cost or congestion of coastal financial centers. Hotels such as The Peninsula Chicago, The American Club in Wisconsin, 21c Museum Hotel Kansas City, Grand Hotel on Mackinac Island, and The St. Paul Hotel provide solid infrastructure, sophisticated meeting spaces, and access to arts and culture, making them suitable for organizations seeking to balance budget discipline with high-quality experiences. Many manufacturing, healthcare, and financial services companies headquartered in Chicago, Minneapolis, Detroit, and other Midwestern cities are increasingly using these properties for retreats that combine operational reviews with leadership development. Readers interested in employment and labor-market trends in these regions can explore usa-update.com/employment and usa-update.com/jobs to understand how regional dynamics influence retreat planning.
Mountain states such as Colorado, Utah, Wyoming, and Montana have emerged as premier destinations for retreats that prioritize wellness, nature, and long-term reflection. Iconic properties including The Broadmoor in Colorado Springs, The St. Regis Aspen Resort, Amangani in Jackson Hole, and Montage Deer Valley in Park City combine state-of-the-art meeting facilities with immediate access to hiking, skiing, and other outdoor pursuits. These venues are particularly well-suited to leadership off-sites focused on long-term strategy, organizational transformation, or culture change, where the physical distance from day-to-day operations helps leaders think more expansively. For organizations in healthcare, life sciences, and professional services, the emphasis on wellness and reflection aligns closely with efforts to prevent burnout and maintain high levels of engagement.
Finally, Hawaii occupies a unique position in the corporate retreat landscape. Properties such as Halekulani in Honolulu, Four Seasons Resort Maui at Wailea, and Mauna Kea Beach Hotel on the Big Island offer a rare combination of natural beauty, cross-cultural learning, and world-class hospitality. For global companies with leadership teams drawn from North America, Asia, and Europe, Hawaii often serves as a geographic and cultural bridge, enabling participants from Tokyo, Singapore, Sydney, London, and New York to converge at a midpoint that is both logistically feasible and emotionally restorative. Business readers who follow international trade, cross-border investment, and multinational strategy can situate these choices within broader global trends on usa-update.com/international.
Corporate Retreat Venue Selector
Select your retreat objective to discover the best US regions and hotel matches
Experience, Expertise, and Trust: What Corporate Clients Expect
Corporate clients in 2026 evaluate retreat venues with a level of rigor that mirrors their evaluation of strategic suppliers. Experience and expertise in handling complex corporate programs are paramount. Properties that regularly host Fortune 500 leadership summits, global sales conferences, or multi-day innovation labs have developed institutional knowledge about the specific needs of corporate clients, from confidentiality requirements and high-security protocols to dietary diversity and accessibility.
Hotels that have built this reputation often highlight their track record with recognizable brands, and while many engagements remain confidential, the patterns are clear: leading technology firms gravitate toward West Coast and mountain properties known for privacy and innovation; global financial institutions continue to favor East Coast and international gateway cities; healthcare and life sciences organizations increasingly choose wellness-focused retreats in Colorado, Arizona, and Hawaii; and energy and industrial companies frequently select Southern and Midwestern venues that align with their operational footprints. Executives who follow sector-specific developments in finance, healthcare, and consumer industries can connect these patterns with broader market trends by reviewing coverage on usa-update.com/finance and usa-update.com/consumer.
Trustworthiness is equally critical. Corporate retreats often involve the discussion of sensitive strategic initiatives, potential acquisitions, restructuring plans, or product roadmaps. Hotels that serve this market have responded by strengthening data security, staff training, and privacy measures. Many partner with recognized cybersecurity and communications providers to ensure that meeting-room networks are segmented, encrypted, and monitored, and that audiovisual systems cannot be easily compromised. Organizations such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology provide widely used frameworks for information security; interested readers can learn more about these standards on the institute's cybersecurity framework page, which many corporate IT departments reference when assessing third-party venues.
Another dimension of trust is health and safety. Even as pandemic-era restrictions have eased, corporate clients continue to expect robust hygiene protocols, air-quality management, and emergency response capabilities. Top properties have institutionalized many of the practices developed during 2020-2022, integrating them into standard operating procedures. Many align their practices with guidance from organizations such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, whose travel and workplace health resources remain a reference point for risk management teams planning large gatherings.
The Economic and Employment Impact of Retreat Tourism
The expansion of corporate retreat activity has had a notable impact on the US hospitality sector and the broader economy. In destinations from Florida and California to Colorado and Hawaii, retreat tourism has become a key driver of revenue, supporting not only hotel operations but also airlines, local restaurants, transportation providers, cultural institutions, and wellness professionals. As corporate travel patterns have stabilized and diversified since 2023, retreat-focused bookings have helped offset shifts in traditional business travel, particularly in industries that have adopted hybrid work and reduced routine commuting between offices.
This growth has also created employment opportunities across multiple skill levels. Event planners, AV technicians, culinary teams, wellness practitioners, local guides, and cultural partners all benefit from the steady flow of corporate groups seeking curated experiences. In cities such as Orlando, Denver, Austin, and Honolulu, local chambers of commerce and tourism authorities have actively promoted retreat tourism as a pillar of economic development, recognizing its relatively high per-visitor spending and its resilience compared to purely leisure travel. Readers who monitor labor-market dynamics and sectoral employment trends can find complementary reporting on usa-update.com/jobs and usa-update.com/employment, where the intersection between hospitality, corporate demand, and regional development is increasingly visible.
From a macroeconomic standpoint, retreat spending contributes to service-sector growth, supports investment in hotel renovations and expansions, and reinforces the United States' position as a global hub for business events. International comparisons with Europe, Asia, and Latin America suggest that the US remains highly competitive in this segment, particularly because of its combination of large domestic corporate demand, world-class infrastructure, and diverse natural and urban environments. Organizations such as the U.S. Travel Association provide data and analysis on business travel and meetings; those interested can explore current reports on the association's business travel insights page.
Global Benchmarking: How US Retreat Venues Compare
As multinational corporations weigh whether to hold retreats in the United States or abroad, they often benchmark US properties against leading venues in Europe, Asia, and Latin America. Alpine resorts in Switzerland and Austria, coastal properties in Italy, Spain, and France, wellness destinations in Thailand and Bali, and urban convention centers in Singapore and Japan all compete with US hotels for global leadership gatherings. Hotels such as Badrutt's Palace Hotel in St. Moritz, Hotel Cipriani in Venice, and Marina Bay Sands in Singapore are frequently cited as benchmarks for service, architecture, and scale, and they have raised expectations globally for what a corporate retreat venue should deliver.
Nevertheless, the United States retains distinct advantages. Its domestic market of large corporations and high-growth scale-ups ensures a steady pipeline of retreat demand, which in turn supports continuous investment in facilities and services. Its network of major international airports in cities such as New York, Los Angeles, San Francisco, Chicago, Miami, Dallas, and Atlanta provides convenient access from Europe, Asia, South America, and the Middle East. Moreover, the sheer variety of landscapes-from New England's historic cities and the Southern coasts to the Rockies and the Pacific islands-allows corporate planners to choose environments that precisely fit their retreat objectives.
Global organizations that regularly compare options across continents often use resources such as the World Travel & Tourism Council's economic impact reports and OECD analyses of tourism and business travel to understand how different regions are evolving. For readers of usa-update.com, such international benchmarks are particularly relevant when evaluating whether to centralize leadership gatherings in the United States or rotate them among global hubs, a decision that intersects with cost structures, carbon footprints, and talent distribution.
Designing Retreats That Deliver Measurable Outcomes
Choosing the right hotel is only one part of building a successful corporate retreat. In 2026, leading organizations are applying the same discipline to retreat design that they apply to product launches or market expansions. This includes defining clear objectives, aligning stakeholders, and establishing metrics for success, whether those metrics relate to strategic clarity, innovation output, employee engagement, or leadership pipeline development.
Many companies now begin retreat planning six to twelve months in advance, working closely with hotel event teams and external facilitators to craft agendas that balance structured work sessions with informal interaction, wellness, and cultural exploration. Strategy-intensive mornings may be followed by smaller breakout sessions in the afternoon, with evenings reserved for shared experiences such as local culinary events, music performances, or curated visits to museums and historical sites. Properties like 21c Museum Hotel Kansas City, for example, integrate contemporary art into the guest experience, allowing companies to use the hotel itself as a setting for discussions about creativity, risk, and cultural change. Readers who track US cultural and entertainment trends can see how such partnerships are evolving on usa-update.com/entertainment.
Another emerging practice is the integration of philanthropic or community-engagement elements into retreat agendas. Companies increasingly seek to align their off-site gatherings with local social or environmental initiatives, whether through volunteering, skills-based support for nonprofits, or contributions to conservation projects. This not only reinforces corporate values but also deepens the connection between visiting teams and host communities. Organizations such as United Way Worldwide and Habitat for Humanity offer structured corporate engagement programs, and their corporate partnership resources and global volunteer initiatives illustrate the kinds of collaborations that retreats can support.
Measurement and follow-up are also gaining prominence. Instead of treating retreats as isolated events, companies are using them as milestones within broader change programs. Pre-retreat surveys, real-time feedback tools, and post-retreat action plans help ensure that insights are translated into concrete initiatives. Hotels that understand this dynamic often provide post-event support, including access to digital content, recordings, and collaborative workspaces that allow teams to continue building on retreat outcomes after returning to their offices or remote locations.
The Role of Hospitality Partners in the Future of Work
Looking ahead to the remainder of the decade, it is increasingly clear that hotels and resorts will play a structural role in the future of work. As hybrid models mature and companies reduce their fixed office footprints in some markets, off-site gatherings will become the primary context in which entire teams come together physically. Hospitality partners that understand this shift are positioning themselves not just as venues but as long-term strategic allies, offering multi-year retreat frameworks, recurring leadership programs, and integrated digital platforms that support collaboration before, during, and after each gathering.
Technological advances will further transform the retreat experience. Artificial intelligence is already being used by some properties to personalize guest services, optimize room assignments, and anticipate dietary or accessibility needs. Over time, AI may also help design retreat agendas based on participant profiles, organizational priorities, and historical data on what formats have produced the best outcomes. Virtual and augmented reality technologies, supported by organizations such as the IEEE through its standards and research on immersive technologies, could enable more sophisticated hybrid experiences, allowing remote participants to engage more fully in on-site activities.
At the same time, the core value of in-person retreats will remain rooted in human connection, trust-building, and shared experience. For readers of usa-update.com, which serves an audience deeply engaged with business, economy, lifestyle, and international developments, this convergence of technology and human interaction is a defining theme. Retreat venues are becoming laboratories for new ways of working, learning, and collaborating, and the hotels highlighted in this article-spanning the East Coast, West Coast, South, Midwest, Mountain States, and Hawaii-are at the forefront of that transformation.
Choosing the Right Retreat Venue for 2026 and Beyond
For executives planning retreats in 2026, the decision-making process should begin with clarity about strategic intent and continue through careful evaluation of regional context, hotel capabilities, technological infrastructure, sustainability credentials, and wellness integration. It is essential to choose partners that can demonstrate experience with similar organizations, a strong commitment to privacy and security, and the flexibility to adapt to changing needs.
The United States offers an exceptional range of options, from the historic elegance of The St. Regis New York, The Pierre, and The Hay-Adams, to the coastal inspiration of The Ritz-Carlton Laguna Niguel, Terranea Resort, and Pelican Hill, the Southern hospitality of The Cloister at Sea Island, The Houstonian, and Four Seasons Orlando, the Midwestern strength of The Peninsula Chicago and The American Club, the mountain serenity of The Broadmoor, The St. Regis Aspen, Amangani, and Montage Deer Valley, and the island renewal of Halekulani, Four Seasons Maui, and Mauna Kea Beach Hotel. Each of these properties brings distinct advantages, and the right choice depends on the organization's culture, objectives, and geographic footprint.
As corporate leaders continue to navigate economic uncertainty, technological disruption, and evolving employee expectations, retreats will remain a crucial mechanism for alignment and renewal. For readers seeking ongoing coverage of how corporate strategy, travel, and lifestyle intersect in the United States and globally, usa-update.com will continue to track developments across business, economy, travel, lifestyle, and international domains, providing the context needed to make informed decisions about where and how to bring teams together in the years ahead.